Pearson Product-Moment Correlation
What does this test do?
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (or Pearson correlation coefficient, for short) is a measure of the strength of a linear association between two variables and is denoted by r. Basically, a Pearson product-moment correlation attempts to draw a line of best fit through the data of two variables, and the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, indicates how far away all these data points are to this line of best fit (i.e., how well the data points fit this new model/line of best fit).
What values can the Pearson correlation coefficient take?
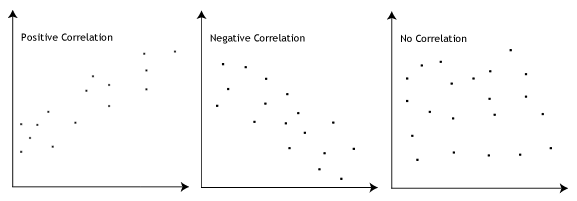
The Pearson correlation coefficient, r, can take a range of values from +1 to -1. A value of 0 indicates that there is no association between the two variables. A value greater than 0 indicates a positive association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, so does the value of the other variable. A value less than 0 indicates a negative association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases. This is shown in the diagram below:
How can we determine the strength of association based on the Pearson correlation coefficient?
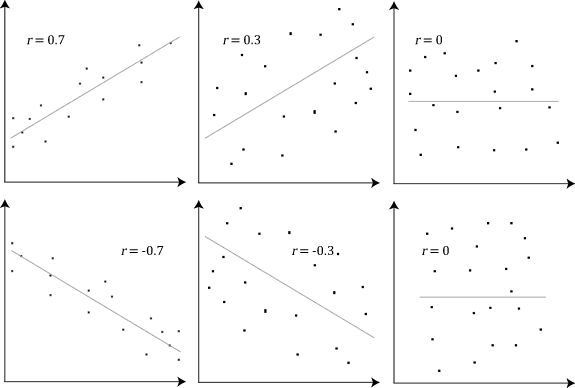
The stronger the association of the two variables, the closer the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, will be to either +1 or -1 depending on whether the relationship is positive or negative, respectively. Achieving a value of +1 or -1 means that all your data points are included on the line of best fit – there are no data points that show any variation away from this line. Values for r between +1 and -1 (for example, r = 0.8 or -0.4) indicate that there is variation around the line of best fit. The closer the value of r to 0 the greater the variation around the line of best fit. Different relationships and their correlation coefficients are shown in the diagram below: