SREERAGAM
My desire is to be a free thinker,finding entertainment in my day to day work and life.Utilize the exposure and knowledge to cater the younger generation.Spread the fragrance of positive energy to the people around me. Sruthi.S
Saturday, February 16, 2019
Friday, November 23, 2018
Pearson Product-Moment Correlation
Pearson Product-Moment Correlation
What does this test do?
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (or Pearson correlation coefficient, for short) is a measure of the strength of a linear association between two variables and is denoted by r. Basically, a Pearson product-moment correlation attempts to draw a line of best fit through the data of two variables, and the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, indicates how far away all these data points are to this line of best fit (i.e., how well the data points fit this new model/line of best fit).
What values can the Pearson correlation coefficient take?
The Pearson correlation coefficient, r, can take a range of values from +1 to -1. A value of 0 indicates that there is no association between the two variables. A value greater than 0 indicates a positive association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, so does the value of the other variable. A value less than 0 indicates a negative association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases. This is shown in the diagram below:
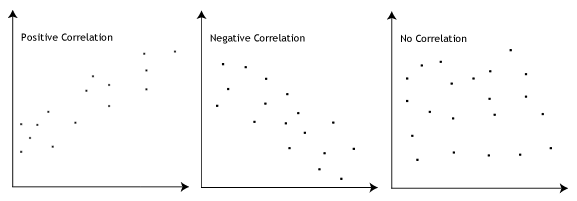
How can we determine the strength of association based on the Pearson correlation coefficient?
The stronger the association of the two variables, the closer the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, will be to either +1 or -1 depending on whether the relationship is positive or negative, respectively. Achieving a value of +1 or -1 means that all your data points are included on the line of best fit – there are no data points that show any variation away from this line. Values for r between +1 and -1 (for example, r = 0.8 or -0.4) indicate that there is variation around the line of best fit. The closer the value of r to 0 the greater the variation around the line of best fit. Different relationships and their correlation coefficients are shown in the diagram below:
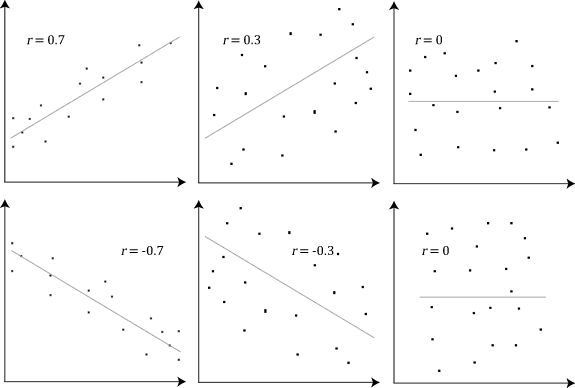
Stanine Scores
What is a Stanine Score?
A stanine (“standard nine”) score is a way to scale scores on a nine-point scale. It can be used to convert any test score to a single-digit score. Like z-scores and t-scores, stanines are a way to assign a number to a member of a group, relative to all members in that group. However, while z-scores and t-scores can be expressed with decimals like 1.2 or 3.25, stanines are always positive whole numbers from 0 to 9.
Stanines are also similar to normal distributions. You can think of these scores as a bell curve that has been sliced up into 9 pieces. These pieces are numbered 1 through 9, starting at the left hand section. However, where a standard normal distribution has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, stanines have a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 2.
What do Stanines mean?
A person with a score of 9 is in the top 4% of the scorers, while a person with a score of 1 is in the bottom 4%. These types of scores allow you to easily tell if a score is below the mean (a score of 5) or above the mean.
How to Convert a Score to a Stanine
Step 1: Rank the scores from lowest to highest.
Step 2: Assign a stanine score to your scores from Step 1:
| Stanine score | Percentage of scores |
| 1 | Bottom 4% |
| 2 | Next bottom 7% |
| 3 | Next bottom 12% |
| 4 | Next Bottom 17% |
| 5 | Middle 20% |
| 6 | Next top 17% |
| 7 | Next top 12% |
| 8 | Next top 7% |
| 9 | Top 4% |
The mean lies in the middle of the fifth stanine, cutting the center 20% into two parts.
Loss of Information
Stanines are a very simple way of categorizing items into top, middle and bottom percentages. This simplicity means that it’s a very imprecise way to measure anything. Everyone in the same stanine receives the same score. For example, a person at the bottom of the 5th is almost 20 percentage points below the person at the top of the 5th. These differences are what is called “loss of information.”
Thursday, November 15, 2018
Saturday, November 10, 2018
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



